
How can Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) help improve perfectionism?
CBT is an evidence-based psychological approach which has been found useful in treating many different problems. Research shows us it is effective in treating depression; anxiety disorders (phobias; panic disorders; Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD); Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD); habit disorders); Body Dysmorphic Disorder; and other problems, such as anger, sleep difficulties, low self-esteem, psychosis, sexual problems and medically unexplained symptoms.
As described in previous parts of this series, perfectionism may be a factor in the development of these problems and also may keep these problems going.
CBT, at a very basic level, aims to understand and make change with thoughts, beliefs and behaviours that keep problems going. In working on perfectionism, these cycles are identified and the aim is to make change to reduce problem areas. Below is an example of a cycle.
Perfectionism Cycle
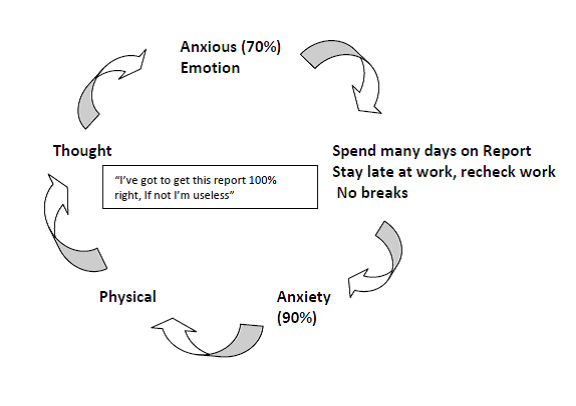 In work with this person, understanding this cycle and making change with thoughts and behaviours is a central piece of work. So challenging the thoughts would involve:
In work with this person, understanding this cycle and making change with thoughts and behaviours is a central piece of work. So challenging the thoughts would involve:
- Does this piece of work need to be done 100%?
- Does it mean you are useless if you don’t achieve 100%?
Work on behaviours would involve goals and experiments on practicing imperfection, such as doing less than 100% and predicting how this would feel for the person, but also what the outcome would be. Could it be the boss doesn’t notice less than 100%? Could it be that 100% in this report was never expected but the person's own unrelenting standards drove them on?
Goals and experiments are set on deliberately making mistakes and leaving tasks incomplete and, again, predicting how this would be and then how it actually was. Other strategies used would focus on engaging and enjoying activity, rather than on achievement. Another plan would be setting goals for more balance in work, play and rest and attributing values to these areas.
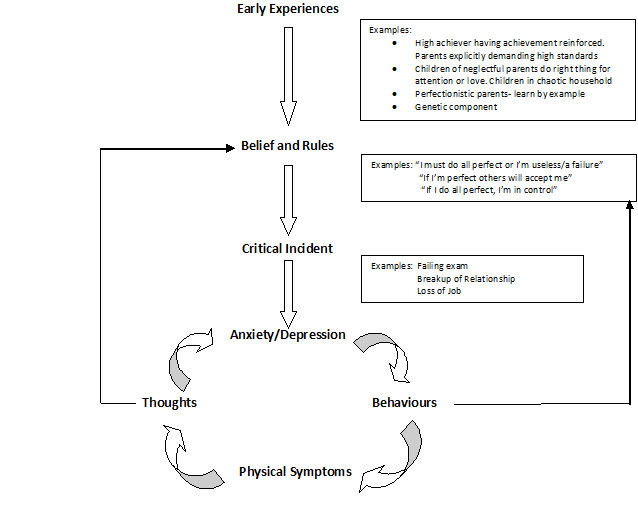
CBT, in the main, focuses on the here and now. The above intervention works on the cycles that are happening now. However, we do look to past early experiences that may have led to beliefs that keep problems going in the here and now. Case formulation is the way we do this. This is useful as it helps someone understand their perfectionism and then how to make change.
Case Formulation
Tags: CBT
Continue to…
Mistreatment of Older People in Ireland

